让你的iOS应用程序支持运行JavaScript脚本:JavaScriptCore框架详解
说到JavaScript脚本,iOS开发者都会想到一个名叫JavaScriptCore的框架。这个框架的确十分强大,其中封装了一套JavaScript运行环境以及Native与JS数据类型之间的转换桥梁。本篇博客主要讨论如何使用此框架来在iOS应用中运行JavaScript脚本。
一、JavaScriptCore框架结构
在学习一个框架时,首先应该先了解整个框架的结构,拿iOS开发来举例,对于一个陌生的框架,第一步需要先搞清楚这里面都包含哪些类,个各类之间是怎样的关系,这个框架和其他的框架间有无联系以及怎样产生的联系。将些问题搞清楚,有了大体上的认识后,我们再来学习其中的每个类即其他细节的应用将非常容易。我们先来看一张JavaScriptCore框架的结构图:
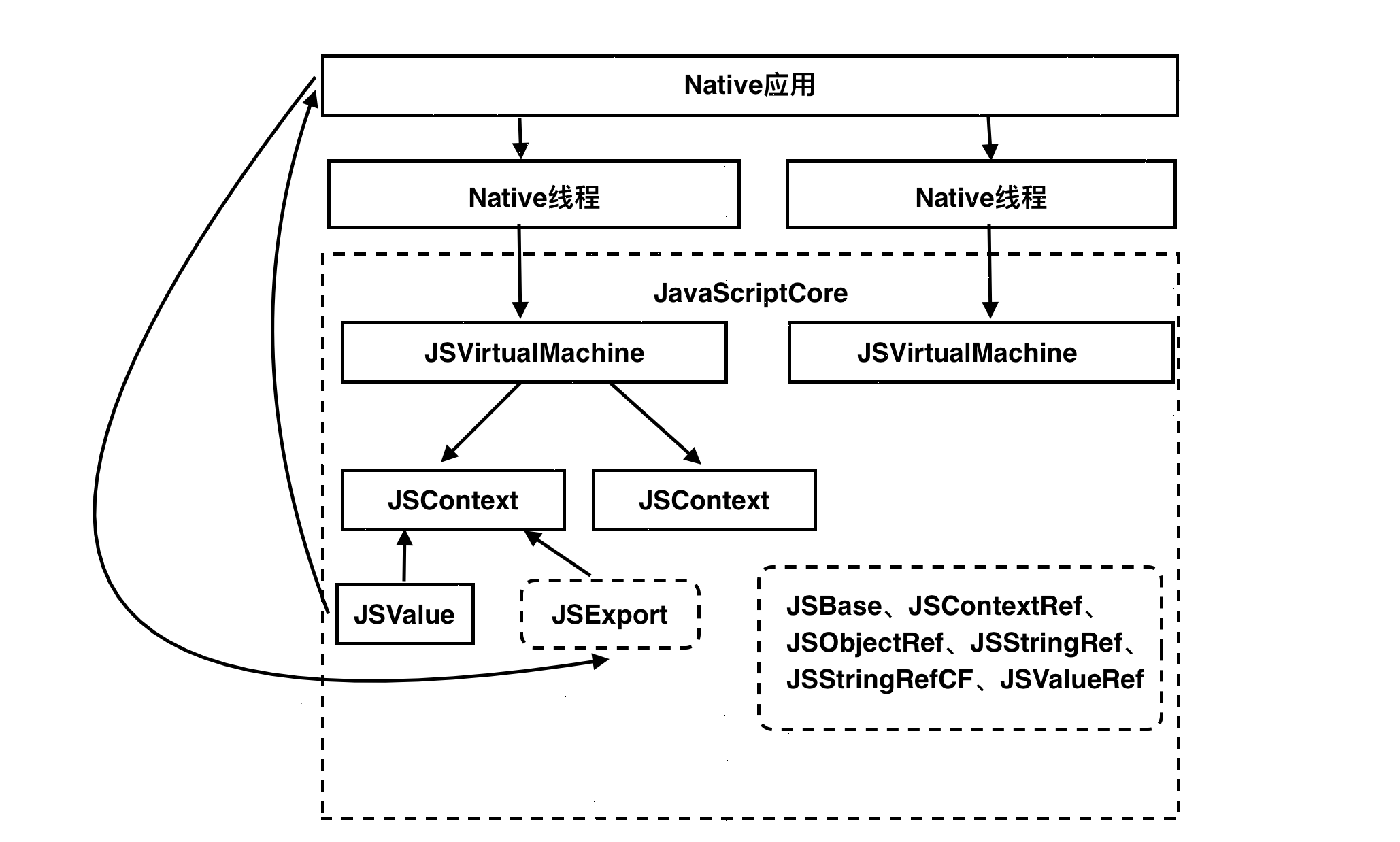
这张图是我手工画的,不是那么美观并且没有文字的解释,但是我觉得它能非常直观的表达JavaScriptCore中包含的类之间的关系。下面我来向你解释这张图究竟表达了什么意思,首先原生的iOS应用是支持多线程执行任务的,我们知道JavaScript是单线程,但这并不代表我们不能在Native中异步执行不同的JavaScript代码。
1.JSVirtualMachine——JavaScript的虚拟机
JavaScriptCore中提供了一个名为JSVirtualMachine的类,顾名思义,这个类可以理解为一个JS虚拟机。在Native中,只要你愿意,你可以创建任意多个JSVirtualMachine对象,各个JSViretualMachine对象间是相互独立的,他们之间不能共享数据也不能传递数据,如果你把他们放在不同的Native线程,他们就可以并行的执行无关的JS任务。
2.JSContext——JavaScript运行环境
JSContext上下文对象可以理解为是JS的运行环境,同一个JSVirtualMachine对象可以关联多个JSContext对象,并且在WebView中每次刷新操作后,此WebView的JS运行环境都是不同的JSContext对象。其作用就是用来执行JS代码,在Native和JS间进行数据的传递。
3.JSValue——JavaScript值对象
JavaScript和Objective-C虽然都是面向对象语言,但其实现机制完全不同,OC是基于类的,JS是基于原型的,并且他们的数据类型间也存在很大的差异。因此若要在Native和JS间无障碍的进行数据的传递,就需要一个中间对象做桥接,这个对象就是JSValue。
4.JSExport
JSExport是一个协议,Native中遵守此解析的类可以将方法和属性转换为JS的接口供JS调用。
5.一些用于C语言的结构
你一定注意到了,上图的右下角还有一块被虚线包围的区域,其中的"类"都是C语言风格,JavaScriptCore框架是支持在Objective-C、Swift和C三种语言中使用的。
二、在Native中运行JavaScript脚本代码
我们先来编写一个最简单的例子,使用OC代码来执行一段JS脚本。首先新建一个文件,将其后缀设置为.js,我这里将它命令为main.js,在其中编写如下代码:
1
2
3
| (function(){
console.log("Hello Native");
})();
|
上面是一个自执行的函数,其中打印了“Hello Native”字符串。在Native中编写如下代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| - (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
NSString * path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"main" ofType:@"js"];
NSData * jsData = [[NSData alloc]initWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSString * jsCode = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:jsData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
self.jsContext = [[JSContext alloc]init];
[self.jsContext evaluateScript:jsCode];
}
|
需要注意,其实这里我将创建的JSContext对象作为了当前视图控制器的属性,这样做的目的仅仅是为了方便调试,不过不对此context对象进行引用,当viewDidLoad函数执行完成后,JS运行环境也将被销毁,我们就无法在Safari中直观的看到JS代码的执行结果了。
运行工程,记得要打开Safari浏览器的自动显示JSContent检查器,如下图:
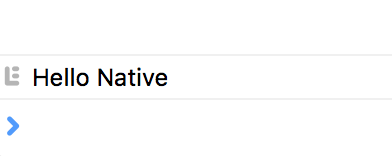
当iOS模拟器跑起来后,Safari会自动弹出开发者工具,在控制台里面可以看到来自JavaScript的真挚问候:
刚才我们只是简单了通过原生调用了一段JS代码,但是如果Native在调JS方法时无法传参那也太low了,我们可以直接将要传递的参数格式化到字符串中,修改main.js文件如下:
1
2
3
4
| function put(name){
console.log("Hello "+name);
};
put(%@);
|
再封装一个OC方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| -(void)runJS_Hello:(NSString *)name{
NSString * path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"main" ofType:@"js"];
NSData * jsData = [[NSData alloc]initWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSString * jsCode = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:jsData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
NSString * finiString = [NSString stringWithFormat:jsCode,name];
[self.jsContext evaluateScript:finiString];
}
|
在viewDidLoad中进行调用,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
| - (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.jsContext = [[JSContext alloc]init];
[self runJS_Hello:@"'阿凡达'"];
}
|
运行再看Safari控制台的结果,编程了Hello 阿凡达~:

其实evaluateScript函数执行后会将JS代码的执行结果进行返回,是JSValue类型的对象,后面会再介绍。
三、在JavaScript中调用Native方法
有来无往非君子,同样也可以在原生中编写方法让JS来调用,示例如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
| - (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
void(^block)() = ^(){
NSLog(@"Hello JavaScript");
};
self.jsContext = [[JSContext alloc]init];
[self.jsContext setObject:block forKeyedSubscript:@"oc_hello"];
}
|
上面setObject:forKeyedSubscript:方法用来向JSContext环境的全局对象中添加属性,这里添加了一个函数属性,取名为oc_hello。这里JavaScriptCore会自动帮我们把一些数据类型进行转换,会将OC的函数转换为JS的函数,运行工程,在Safari的控制台中调用oc_hello函数,可以看到在Xcode控制台输出了对JavaScript的真挚问候,如下:

同样,如果声明的block是带参数的,JS在调用此OC方法时也需要传入参数,如果block有返回值,则在JS中也能获取到返回值,例如:
1
2
3
4
5
6
| BOOL (^block)(NSString *) = ^(NSString *name){
NSLog(@"%@", [NSString stringWithFormat:@"Hello %@",name]);
return YES;
};
self.jsContext = [[JSContext alloc]init];
[self.jsContext setObject:block forKeyedSubscript:@"oc_hello"];
|
四、深入JSContext类
看到这,你已经学会最基础的OC与JS互相问好(交互)。下面我们再来深入看下JSContext中的属性和方法。
创建JSContext对象有如下两种方式:
1
2
3
4
|
- (instancetype)init;
- (instancetype)initWithVirtualMachine:(JSVirtualMachine *)virtualMachine;
|
执行JS代码有如下两个方法:
1
2
3
4
|
- (JSValue *)evaluateScript:(NSString *)script;
- (JSValue *)evaluateScript:(NSString *)script withSourceURL:(NSURL *)sourceURL NS_AVAILABLE(10_10, 8_0);
|
下面的属性和方法可以获取到JS运行环境中的一些信息:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
+ (JSContext *)currentContext;
+ (JSValue *)currentCallee;
+ (JSValue *)currentThis;
+ (NSArray *)currentArguments;
@property (readonly, strong) JSValue *globalObject;
@property (strong) JSValue *exception;
@property (copy) void(^exceptionHandler)(JSContext *context, JSValue *exception);
@property (readonly, strong) JSVirtualMachine *virtualMachine;
@property (copy) NSString *name;
- (JSValue *)objectForKeyedSubscript:(id)key;
- (void)setObject:(id)object forKeyedSubscript:(NSObject <NSCopying> *)key;
+ (JSContext *)contextWithJSGlobalContextRef:(JSGlobalContextRef)jsGlobalContextRef;
@property (readonly) JSGlobalContextRef JSGlobalContextRef;
|
五、深入JSValue类
JSValue是JavaScript与Objective-C之间的数据桥梁。在Objective-C中调用JS脚本或者JS调用OC方法都可以使用JSValue来传输数据。其中属性和方法示例如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
@property (readonly, strong) JSContext *context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithObject:(id)value inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithBool:(BOOL)value inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithDouble:(double)value inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithInt32:(int32_t)value inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithUInt32:(uint32_t)value inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithNewObjectInContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithNewArrayInContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithNewRegularExpressionFromPattern:(NSString *)pattern flags:(NSString *)flags inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithNewErrorFromMessage:(NSString *)message inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithNullInContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithUndefinedInContext:(JSContext *)context;
|
JavaScript中的数据类型和Objective-C的数据类型还是有着很大的差异,其中对应关系如下:
| Objective-C | JavaScript |
| nil | undefined |
| NSNull | null |
| NSString | string |
| NSNumber | number boolean |
| NSDictionary | Object |
| NSArray | Array |
| NSDate | Date |
| Block | Function |
| id | Object |
| Class | Object |
下面这些方法可以将JSValue值转换为Objective-C中的数据类型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
|
- (id)toObject;
- (id)toObjectOfClass:(Class)expectedClass;
- (BOOL)toBool;
- (double)toDouble;
- (int32_t)toInt32;
- (uint32_t)toUInt32;
- (NSNumber *)toNumber;
- (NSString *)toString;
- (NSDate *)toDate;
- (NSArray *)toArray;
- (NSDictionary *)toDictionary;
- (JSValue *)valueForProperty:(NSString *)property;
- (void)setValue:(id)value forProperty:(NSString *)property;
- (BOOL)deleteProperty:(NSString *)property;
- (BOOL)hasProperty:(NSString *)property;
- (void)defineProperty:(NSString *)property descriptor:(id)descriptor;
- (JSValue *)valueAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index;
- (void)setValue:(id)value atIndex:(NSUInteger)index;
@property (readonly) BOOL isUndefined;
@property (readonly) BOOL isNull;
@property (readonly) BOOL isBoolean;
@property (readonly) BOOL isNumber;
@property (readonly) BOOL isString;
@property (readonly) BOOL isObject;
@property (readonly) BOOL isArray;
@property (readonly) BOOL isDate;
- (BOOL)isEqualToObject:(id)value;
- (BOOL)isEqualWithTypeCoercionToObject:(id)value;
- (BOOL)isInstanceOf:(id)value;
- (JSValue *)callWithArguments:(NSArray *)arguments;
- (JSValue *)constructWithArguments:(NSArray *)arguments;
- (JSValue *)invokeMethod:(NSString *)method withArguments:(NSArray *)arguments;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithPoint:(CGPoint)point inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithRange:(NSRange)range inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithRect:(CGRect)rect inContext:(JSContext *)context;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithSize:(CGSize)size inContext:(JSContext *)context;
- (CGPoint)toPoint;
- (NSRange)toRange;
- (CGRect)toRect;
- (CGSize)toSize;
+ (JSValue *)valueWithJSValueRef:(JSValueRef)value inContext:(JSContext *)context;
|
其实在JavaScriptCore框架中还有一个JSManagerValue类,这个的主要作用是管理内存。虽然我们在编写Objective-C代码时有强大的自动引用技术(ARC技术),我们一般无需关心对象的内存问题,在编写JavaScript代码时也有强大的垃圾回收机制(这种机制下甚至连循环引用都不是问题),但是在OC和JS混合开发时,就很容易出现问题了,比如一个JS垃圾回收机制释放掉的对象OC中却还在用,反过来也是一样。JSManagerValue对JSValue进行了一层包装,它可以保证在适合时候使用这个对象时对象都不会被释放,其中方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
+ (JSManagedValue *)managedValueWithValue:(JSValue *)value;
+ (JSManagedValue *)managedValueWithValue:(JSValue *)value andOwner:(id)owner;
- (instancetype)initWithValue:(JSValue *)value;
@property (readonly, strong) JSValue *value;
|
六、Objective-C与JavaScript复杂对象的映射
我们在使用JavaScript调用Objective-C方法的实质是将一个OC函数设置为了JS全局对象的一个属性,当然我们也可以设置非函数的属性或者任意JSValue(或者可以转换为JSValue)的值。例如:
1
2
3
| self.jsContext = [[JSContext alloc]init];
[self.jsContext setObject:@"iOS" forKeyedSubscript:@"deviceType"];
|
但是如果我们想把OC自定义的一个类的对象设置为JS全局对象的某个属性,JS和OC有着完全不同的对象原理,如果不做任何处理,JS是接收不到OC对象中定义的属性和方法的。这时就需要使用到前面提到的JSExport协议,需要注意,这个协议不是用来被类遵守的,它里面没有规定任何方法,其是用来被继承定义新的协议的,自定义的协议中约定的方法和属性可以在JS中被获取到,示例如下:
OC中新建一个自定义的类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
| @protocol MyObjectProtocol <JSExport>
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSString * name;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSString * subject;
@property(nonatomic,assign)NSInteger age;
-(void)sayHi;
@end
@interface MyObject : NSObject<MyObjectProtocol>
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSString * name;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSString * subject;
@property(nonatomic,assign)NSInteger age;
@end
@implementation MyObject
-(void)sayHi{
NSLog(@"Hello JavaScript");
}
@end
|
添加到JS全局对象中:
1
2
3
4
5
| MyObject* object = [MyObject new];
object.name = @"Jaki";
object.age = 25;
object.subject = @"OC";
[jsContext setObject:object forKeyedSubscript:@"deviceObject"];
|
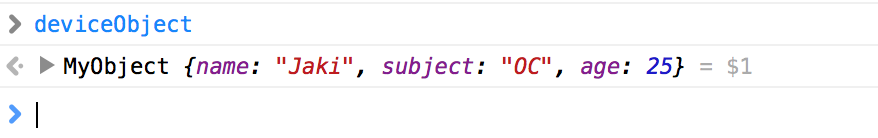
在JS运行环境中可以完整的到deviceObject对象,如下:
七、C语言风格的API解释
JavaScriptCore框架中除了包含完整的Objective-C和Swift语言的API外,也提供了对C语言的支持。
与JS运行环境相关的方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
|
JSContextGroupRef JSContextGroupCreate(void);
JSContextGroupRef JSContextGroupRetain(JSContextGroupRef group);
void JSContextGroupRelease(JSContextGroupRef group);
JSGlobalContextRef JSGlobalContextCreate(JSClassRef globalObjectClass);
JSGlobalContextRef JSGlobalContextCreateInGroup(JSContextGroupRef group, JSClassRef globalObjectClass);
JSGlobalContextRef JSGlobalContextRetain(JSGlobalContextRef ctx);
void JSGlobalContextRelease(JSGlobalContextRef ctx);
JSObjectRef JSContextGetGlobalObject(JSContextRef ctx);
JSContextGroupRef JSContextGetGroup(JSContextRef ctx);
JSGlobalContextRef JSContextGetGlobalContext(JSContextRef ctx);
JSStringRef JSGlobalContextCopyName(JSGlobalContextRef ctx);
void JSGlobalContextSetName(JSGlobalContextRef ctx, JSStringRef name);
|
与定义JS对象的相关方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
|
JSClassRef JSClassCreate(const JSClassDefinition* definition);
JSClassRef JSClassRetain(JSClassRef jsClass);
void JSClassRelease(JSClassRef jsClass);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMake(JSContextRef ctx, JSClassRef jsClass, void* data);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeFunctionWithCallback(JSContextRef ctx, JSStringRef name, JSObjectCallAsFunctionCallback callAsFunction);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeConstructor(JSContextRef ctx, JSClassRef jsClass, JSObjectCallAsConstructorCallback callAsConstructor);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeArray(JSContextRef ctx, size_t argumentCount, const JSValueRef arguments[], JSValueRef* exception);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeDate(JSContextRef ctx, size_t argumentCount, const JSValueRef arguments[], JSValueRef* exception);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeError(JSContextRef ctx, size_t argumentCount, const JSValueRef arguments[], JSValueRef* exception);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeRegExp(JSContextRef ctx, size_t argumentCount, const JSValueRef arguments[], JSValueRef* exception);
JSObjectRef JSObjectMakeFunction(JSContextRef ctx, JSStringRef name, unsigned parameterCount, const JSStringRef parameterNames[], JSStringRef body, JSStringRef sourceURL, int startingLineNumber, JSValueRef* exception);
JSValueRef JSObjectGetPrototype(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object);
void JSObjectSetPrototype(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, JSValueRef value);
bool JSObjectHasProperty(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, JSStringRef propertyName);
JSValueRef JSObjectGetProperty(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, JSStringRef propertyName, JSValueRef* exception);
void JSObjectSetProperty(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, JSStringRef propertyName, JSValueRef value, JSPropertyAttributes attributes, JSValueRef* exception);
bool JSObjectDeleteProperty(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, JSStringRef propertyName, JSValueRef* exception);
JSValueRef JSObjectGetPropertyAtIndex(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, unsigned propertyIndex, JSValueRef* exception);
void JSObjectSetPropertyAtIndex(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, unsigned propertyIndex, JSValueRef value, JSValueRef* exception);
void* JSObjectGetPrivate(JSObjectRef object);
bool JSObjectSetPrivate(JSObjectRef object, void* data);
bool JSObjectIsFunction(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object);
JSValueRef JSObjectCallAsFunction(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, JSObjectRef thisObject, size_t argumentCount, const JSValueRef arguments[], JSValueRef* exception);
bool JSObjectIsConstructor(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object);
JSObjectRef JSObjectCallAsConstructor(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object, size_t argumentCount, const JSValueRef arguments[], JSValueRef* exception);
JSPropertyNameArrayRef JSObjectCopyPropertyNames(JSContextRef ctx, JSObjectRef object);
JSPropertyNameArrayRef JSPropertyNameArrayRetain(JSPropertyNameArrayRef array);
void JSPropertyNameArrayRelease(JSPropertyNameArrayRef array);
size_t JSPropertyNameArrayGetCount(JSPropertyNameArrayRef array);
JSStringRef JSPropertyNameArrayGetNameAtIndex(JSPropertyNameArrayRef array, size_t index);
void JSPropertyNameAccumulatorAddName(JSPropertyNameAccumulatorRef accumulator, JSStringRef propertyName);
|
JS数据类型相关定义在JSValueRef中,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
|
JSType JSValueGetType(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef);
bool JSValueIsUndefined(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsNull(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsBoolean(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsNumber(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsString(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsObject(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsObjectOfClass(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value, JSClassRef jsClass);
bool JSValueIsArray(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsDate(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
bool JSValueIsEqual(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef a, JSValueRef b, JSValueRef* exception);
bool JSValueIsStrictEqual(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef a, JSValueRef b);
bool JSValueIsInstanceOfConstructor(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value, JSObjectRef constructor, JSValueRef* exception);
JSValueRef JSValueMakeUndefined(JSContextRef ctx);
JSValueRef JSValueMakeNull(JSContextRef ctx);
JSValueRef JSValueMakeBoolean(JSContextRef ctx, bool boolean);
JSValueRef JSValueMakeNumber(JSContextRef ctx, double number);
JSValueRef JSValueMakeString(JSContextRef ctx, JSStringRef string);
JSValueRef JSValueMakeFromJSONString(JSContextRef ctx, JSStringRef string);
JSStringRef JSValueCreateJSONString(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value, unsigned indent, JSValueRef* exception);
bool JSValueToBoolean(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value);
double JSValueToNumber(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value, JSValueRef* exception);
JSStringRef JSValueToStringCopy(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value, JSValueRef* exception);
JSObjectRef JSValueToObject(JSContextRef ctx, JSValueRef value, JSValueRef* exception);
|
在C风格的API中,字符串也被包装成了JSStringRef类型,其中方法如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
JSStringRef JSStringCreateWithCharacters(const JSChar* chars, size_t numChars);
JSStringRef JSStringCreateWithUTF8CString(const char* string);
JSStringRef JSStringRetain(JSStringRef string);
void JSStringRelease(JSStringRef string);
size_t JSStringGetLength(JSStringRef string);
size_t JSStringGetUTF8CString(JSStringRef string, char* buffer, size_t bufferSize);
bool JSStringIsEqual(JSStringRef a, JSStringRef b);
bool JSStringIsEqualToUTF8CString(JSStringRef a, const char* b);
|
八、Hybird App 构建思路
Hybird App是指混合模式移动应用,即其中既包含原生的结构有内嵌有Web的组件。这种App不仅性能和用户体验可以达到和原生所差无几的程度,更大的优势在于bug修复快,版本迭代无需发版。3月8日苹果给许多开发者发送了一封警告邮件,主要是提示开发者下载脚本动态更改App原本行为的做法将会被提审拒绝。其实这次邮件所提内容和Hybird App并无太大关系(对ReactNative也没有影响),苹果警告的是网络下发脚本并且使用runtime动态修改Native行为的应用,Hybird App的实质并没有修改原Native的行为,而是将下发的资源进行加载和界面渲染,类似WebView。
关于混合开发,我们有两种模式:
1.Native内嵌WebView,通过JS与OC交互实现业务无缝的衔接。
无论是UIWebView还是WKWebKit,我们都可以在其中拿到当前的JSContext,然是使用前面介绍的方法便可以实现数据互通与交互。这种方式是最简单的混合开发,但其性能和原生相比要差一些。示意图如下:
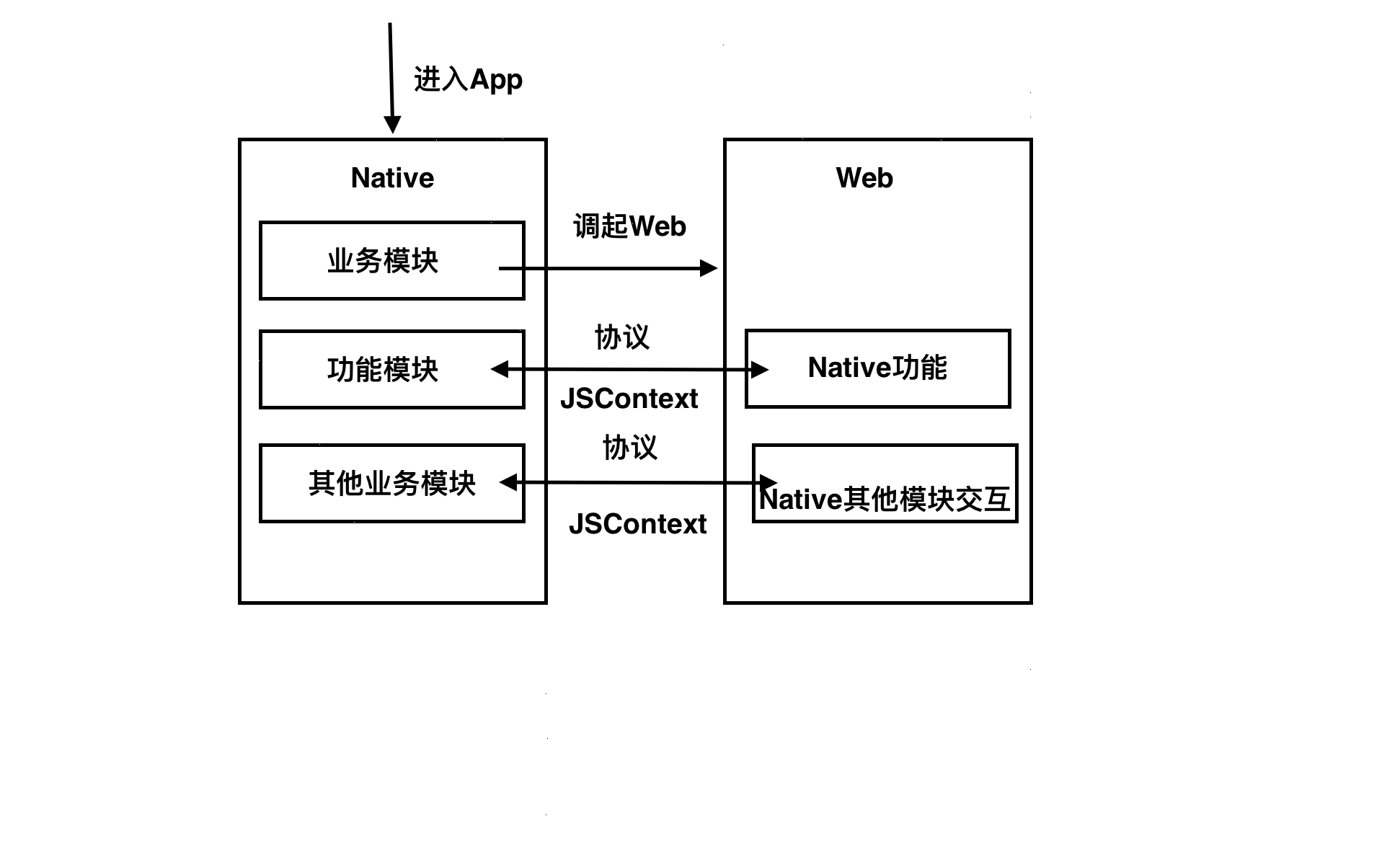
2.下发JS脚本,使用类似ReactNative的框架进行原生渲染
这是一种效率非常高的混合开发模式,并且ReactNative也本身支持android和iOS公用一套代码。我们也可以使用JavaScriptCore自己实现一套解析逻辑,使用JavaScript来编写Native应用,要完整实现这样一套东西太复杂了,我们也没有能力完成一个如此庞大的工程,但是我们可以做一个小Demo来模拟其原理,这样可以更好的帮助我们理解Hybird App的构建原理。
我们打算实现这样的功能:通过下发JS脚本创建原生的UILabel标签与UIButton控件,首先编写JS代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| (function(){
console.log("ProgectInit");
return render();
})();
function Label(rect,text,color){
this.rect = rect;
this.text = text;
this.color = color;
this.typeName = "Label";
}
function Button(rect,text,callFunc){
this.rect = rect;
this.text = text;
this.callFunc = callFunc;
this.typeName = "Button";
}
function Rect(x,y,width,height){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
this.width = width;
this.height = height;
}
function Color(r,g,b,a){
this.r = r;
this.g = g;
this.b = b;
this.a = a;
}
function render(){
var rect = new Rect(20,100,280,30);
var color = new Color(1,0,0,1);
var label = new Label(rect,"Hello World",color);
var rect2 = new Rect(20,150,280,30);
var color2 = new Color(0,1,0,1);
var label2 = new Label(rect2,"Hello Native",color2);
var rect3 = new Rect(20,200,280,30);
var color3 = new Color(0,0,1,1);
var label3 = new Label(rect3,"Hello JavaScript",color3);
var rect4 = new Rect(20,240,280,30);
var button = new Button(rect4,"我是一个按钮",function(){
var randColor = new Color(Math.random(),Math.random(),Math.random(),1);
Globle.changeBackgroundColor(randColor);
});
return [label,label2,label3,button];
}
|
创建一个Objective-C类绑定到JS全局对象上,作为OC方法的桥接器:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
|
#import <Foundation/Foundation.h>
#import <UIKit/UIKit.h>
#import <JavaScriptCore/JavaScriptCore.h>
@protocol GloblePrptocol <JSExport>
-(void)changeBackgroundColor:(JSValue *)value;
@end
@interface Globle : NSObject<GloblePrptocol>
@property(nonatomic,weak)UIViewController * ownerController;
@end
#import "Globle.h"
@implementation Globle
-(void)changeBackgroundColor:(JSValue *)value{
self.ownerController.view.backgroundColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:value[@"r"].toDouble green:value[@"g"].toDouble blue:value[@"b"].toDouble alpha:value[@"a"].toDouble];
}
@end
|
在ViewController中实现一个界面渲染的render解释方法,并建立按钮的方法转换,如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
|
#import "ViewController.h"
#import <JavaScriptCore/JavaScriptCore.h>
#import "Globle.h"
@interface ViewController ()
@property(nonatomic,strong)JSContext * jsContext;
@property(nonatomic,strong)NSMutableArray * actionArray;
@property(nonatomic,strong)Globle * globle;
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
self.jsContext = [JSContext new];
self.globle = [Globle new];
self.globle.ownerController = self;
self.jsContext[@"Globle"] = self.globle;
self.actionArray = [NSMutableArray array];
[self render];
}
-(void)render{
NSString * path = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"main" ofType:@"js"];
NSData * jsData = [[NSData alloc]initWithContentsOfFile:path];
NSString * jsCode = [[NSString alloc]initWithData:jsData encoding:NSUTF8StringEncoding];
JSValue * jsVlaue = [self.jsContext evaluateScript:jsCode];
for (int i=0; i<jsVlaue.toArray.count; i++) {
JSValue * subValue = [jsVlaue objectAtIndexedSubscript:i];
if ([[subValue objectForKeyedSubscript:@"typeName"].toString isEqualToString:@"Label"]) {
UILabel * label = [UILabel new];
label.frame = CGRectMake(subValue[@"rect"][@"x"].toDouble, subValue[@"rect"][@"y"].toDouble, subValue[@"rect"][@"width"].toDouble, subValue[@"rect"][@"height"].toDouble);
label.text = subValue[@"text"].toString;
label.textColor = [UIColor colorWithRed:subValue[@"color"][@"r"].toDouble green:subValue[@"color"][@"g"].toDouble blue:subValue[@"color"][@"b"].toDouble alpha:subValue[@"color"][@"a"].toDouble];
[self.view addSubview:label];
}else if ([[subValue objectForKeyedSubscript:@"typeName"].toString isEqualToString:@"Button"]){
UIButton * button = [UIButton buttonWithType:UIButtonTypeSystem];
button.frame = CGRectMake(subValue[@"rect"][@"x"].toDouble, subValue[@"rect"][@"y"].toDouble, subValue[@"rect"][@"width"].toDouble, subValue[@"rect"][@"height"].toDouble);
[button setTitle:subValue[@"text"].toString forState:UIControlStateNormal];
button.tag = self.actionArray.count;
[button addTarget:self action:@selector(buttonAction:) forControlEvents:UIControlEventTouchUpInside];
[self.actionArray addObject:subValue[@"callFunc"]];
[self.view addSubview:button];
}
}
}
-(void)buttonAction:(UIButton *)btn{
JSValue * action = self.actionArray[btn.tag];
[action callWithArguments:nil];
}
@end
|
运行工程,效果如下图所示,点击按钮即可实现简单的界面颜色切换:

上面的示例工程我只实现了UILabel类与UIButton类的JS-OC转换,如果将原生控件和JS对象再进行一层绑定,并且实现大部分JS类与原生类和他们内部的属性,则我们就开发了一套Hybird App开发框架,但并没有这个必要,如果你对更多兴趣,可以深入学习下ReactNative。
文中的示例Demo我放在了Github上,地址如下:[https://github.com/ZYHshao/Demo-Hybird](https://github.com/ZYHshao/Demo-Hybird)。
前端学习新人,有志同道合的朋友,欢迎交流与指导,QQ群:541458536







